External Access
This section deals with configuring your network to allow access to your Vesta from the outside world. This is useful if you want to monitor conditions when you're away from home, for instance. It's also necessary for remote maintenance and troubleshooting.
If you choose to enable remote access, this section describes the required steps.
This requires that networking is properly configured on the Vesta controller itself. In particular, the gateway and DNS server addresses must be correct for your network. In most cases this will be set up prior to delivery.
External access is accomplished by configuring the router on your network. The router is sometimes a separate device, and sometimes it's built into the cable or DSL modem. It is the device that sits between your network and the outside world. There are almost limitless network configurations, and this page will not attempt to anticipate all of them. We'll describe the process for a typical configuration and provide links to resources that can help you with your specific situation.
Typical Network
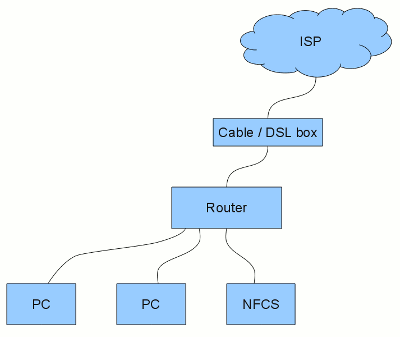
Most networks have a device that provides a connection to the Internet via an Internet Service Provider (ISP). This device is often referred to as a cable or DSL modem. There is usually another device called a router which allows multiple devices to access the Internet and share the single IP address provided by the ISP.
Many companies make routers. Some of the more common are Linksys, Netgear, and Dlink. Often the router functionality is contained within the cable/DSL modem. In that case, the cable/DSL box will have multiple Ethernet ports. The diagram at the right shows the components in a typical home or small office network.
Port Forwarding
In order for external access to work, we have to establish port forwarding. All Internet communications utilize ports that provide the actual connection between computers. the Vesta controller uses three ports. These need to be connected through the router to the outside world. This is accomplished by configuring the router. Each brand of router differs in the exact procedure, but the steps tend to be very similar. The most common use of port forwarding is for gaming, and port forwarding instructions often assume that's what you're doing.
There are many resources on the web to help with this. One of the more comprehensive is portforward.com. They have software that they'd like to sell you, but if you click past that they have lots of resources. Their assumption is that you're setting up an Internet multiplayer game, but the process is the same. Just specify that the 'game' you're interested in is http and you'll be set.
In our example we have a Linksys WRT330N router. First step is to find the router on our network. It will often be at address '1' on whatever network address block is in use. If your computer and the Vesta controller have addresses in the form of 192.168.1.x, the router will probably be at 192.168.1.1 - enter this address into the URL bar on your browser. You'll likely get a popup looking for a username and password. Consult your router documentation (or Google) to find the username and password for your router. If the router is built into your cable/DSL modem, you may have to talk to your ISP. They should understand what you're doing and be able to help you.
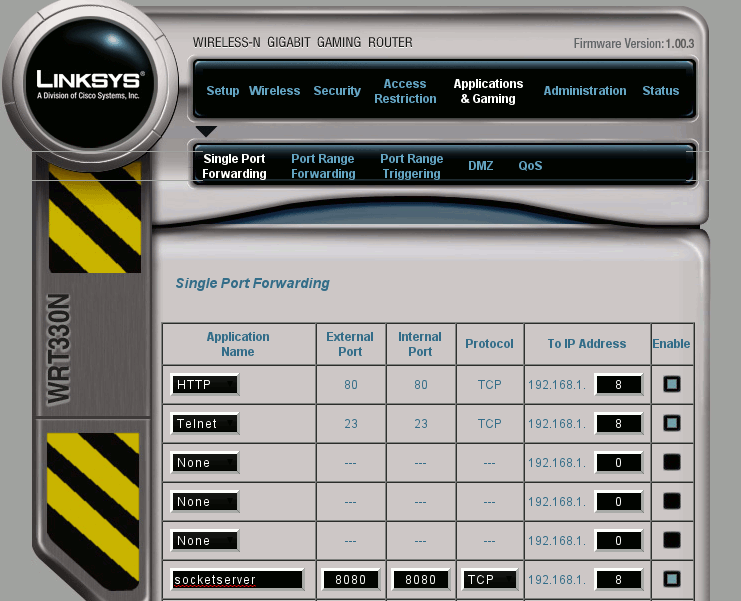
Once you're logged into the router, look for the page that allows you to set up port forwarding. On some Linksys models including the WRT330N that we're using in this example, port forwarding is under 'Applications & Gaming'. We need to set up three ports:
Vesta Classic Ports
- Port 80 for HTTP - allows you to access the Vesta controller user interface from remote browsers, including smart phones.
- Port 23 for Telnet - allows for remote maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Port 7280 for socket server - allows more sophisticated remote access and control. Optional - enable only if you know that you need it.
Vesta Vantage and Pro Ports
- Port 80 for HTTP - allows you to access the Vesta controller user interface from remote browsers, including smart phones.
- Port 22 for SSH - allows for remote maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Port 7280 for socket server - allows more sophisticated remote access and control. Optional - enable only if you know that you need it.
For each port, there are several values that you can set. The exact list varies from router to router.'Name' or 'Application name' doesn't matter, although some routers have predefined names that set up the correct ports for common services such as http, telnet, and ssh. If your router lets you select both external and internal ports, set them to the same values. The protocol is 'TCP' for all three Vesta services. The internal IP address is the IP adress of the Vesta controller. This is the address you use to view the Vesta controller. It's on the inside of the front cover. Make sure that the 'enable' box is checked if present. In the example below, the WRT330N has been set up to forward ports 23, 80, and 7280 to the Vesta controller which is at IP address 192.168.1.8 - this is typical of most router port forwarding setups.
There's generally a button near the bottom of the page to apply your changes. Make sure you click this button. It will usually reboot the router, afetr which you should be able to access your Vesta from outside, using your external IP address.
